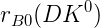Difference: GammaFromTrees (r20 vs. r19)
Gamma Combination from the UTfit group
We use the relevant post-CKM 2012 HFAG averages as inputs. The results of combination:
 system:
system:
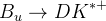 system:
system:
 system:
system:
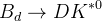 system:
system:
| Parameter | Full fit |
|---|---|
![\gamma [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_d441395f3c6b5d6d14b98a13ae4b8837.png) |  |
![\delta_{B}(DK) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41e661b01cefdd9ec2084738b64160f3.png) |  |
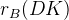 | 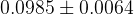 |
![\delta_{B}(DK^{*}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_1baa48393b03b96f22571066583a25b8.png) | 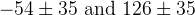 |
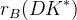 |  |
![\delta_{B}(D^{*}K) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_5211b61dcb830d9a98ee9a7878d74aff.png) |  |
 |  |
![\delta_{B0}(DK^{0}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_060131b4fd1a7430d5cc8dca6c37fdf8.png) | 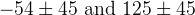 |
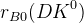 | 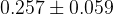 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
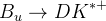 system:
system:
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
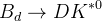 system:
system:
|
|
We use the relevant post-CKM 2012 HFAG averages as inputs. The results of combination:
 system:
system:
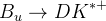 system:
system:
 system:
system:
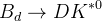 system:
system:
| Parameter | Full fit |
|---|---|
![\gamma [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_d441395f3c6b5d6d14b98a13ae4b8837.png) |  |
![\delta_{B}(DK) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41e661b01cefdd9ec2084738b64160f3.png) |  |
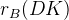 | 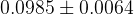 |
![\delta_{B}(DK^{*}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_1baa48393b03b96f22571066583a25b8.png) | 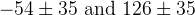 |
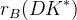 |  |
![\delta_{B}(D^{*}K) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_5211b61dcb830d9a98ee9a7878d74aff.png) |  |
 |  |
![\delta_{B0}(DK^{0}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_060131b4fd1a7430d5cc8dca6c37fdf8.png) | 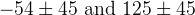 |
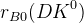 | 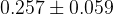 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
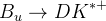 system:
system:
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
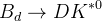 system:
system:
|
|
We use the relevant post-ICHEP 2012 HFAG averages as inputs. The results of combination:
 system:
system:
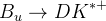 system:
system:
 system:
system:
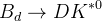 system:
system:
| Parameter | Full fit |
|---|---|
![\gamma [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_d441395f3c6b5d6d14b98a13ae4b8837.png) |  |
![\delta_{B}(DK) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41e661b01cefdd9ec2084738b64160f3.png) | 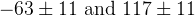 |
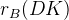 |  |
![\delta_{B}(DK^{*}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_1baa48393b03b96f22571066583a25b8.png) | 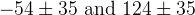 |
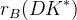 |  |
![\delta_{B}(D^{*}K) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_5211b61dcb830d9a98ee9a7878d74aff.png) |  |
 |  |
![\delta_{B0}(DK^{0}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_060131b4fd1a7430d5cc8dca6c37fdf8.png) |  |
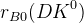 | 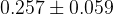 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
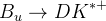 system:
system:
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
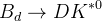 system:
system:
|
|
| Parameter | Full fit |
|---|---|
 | 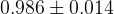 |
 | 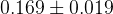 |
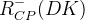 | 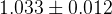 |
 | 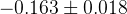 |
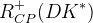 |  |
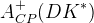 |  |
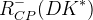 |  |
 |  |
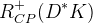 | 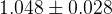 |
 | 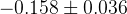 |
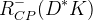 |  |
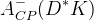 |  |
 | 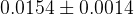 |
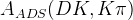 |  |
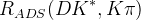 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
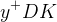 | 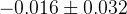 |
 |  |
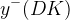 | 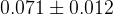 |
 | 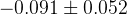 |
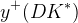 |  |
 |  |
 | 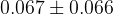 |
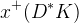 | 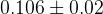 |
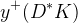 |  |
 | 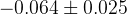 |
 |  |
We use the relevant post-ICHEP 2012 HFAG averages as inputs. The results of combination:
 system:
system:
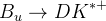 system:
system:
 system:
system:
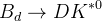 system:
system:
| Parameter | Full fit |
|---|---|
![\gamma [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_d441395f3c6b5d6d14b98a13ae4b8837.png) |  |
![\delta_{B}(DK) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41e661b01cefdd9ec2084738b64160f3.png) | 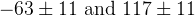 |
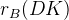 |  |
![\delta_{B}(DK^{*}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_1baa48393b03b96f22571066583a25b8.png) | 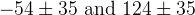 |
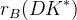 |  |
![\delta_{B}(D^{*}K) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_5211b61dcb830d9a98ee9a7878d74aff.png) |  |
 |  |
![\delta_{B0}(DK^{0}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_060131b4fd1a7430d5cc8dca6c37fdf8.png) |  |
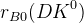 | 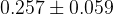 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
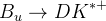 system:
system:
|
|
|
 system:
system:
|
|
|
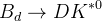 system:
system:
|
|
| Parameter | Full fit |
|---|---|
 | 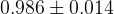 |
 | 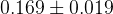 |
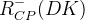 | 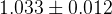 |
 | 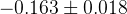 |
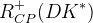 |  |
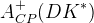 |  |
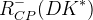 |  |
 |  |
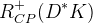 | 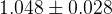 |
 | 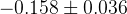 |
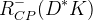 |  |
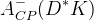 |  |
 | 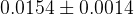 |
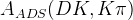 |  |
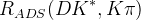 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
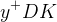 | 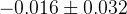 |
 |  |
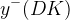 | 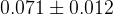 |
 | 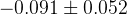 |
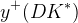 |  |
 |  |
 | 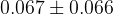 |
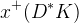 | 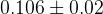 |
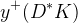 |  |
 | 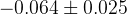 |
 |  |
The angle  of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing
of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing  and
and  mediated transitions in
mediated transitions in  decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams:
decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams: 
 decay:
decay:  and the relative
and the relative  conserving phase
conserving phase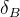 between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the
between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the  decay under investigation.
decay under investigation.
 of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing
of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing  and
and  mediated transitions in
mediated transitions in  decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams:
decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams: 
 decay:
decay: - a singly Cabibbo-suppressed CP eigenstate, like
 for Gronau-London-Wyler (GLW) method;
for Gronau-London-Wyler (GLW) method; - a doubly Cabibbo-suppressed flavor eigenstate, like
 for Atwood-Dunietz-Soni (ADS) method;
for Atwood-Dunietz-Soni (ADS) method; - a Cabibbo-allowed self-conjugate 3-body state, like
 for Giri-Grossman-Soffer-Zupan (GGSZ) method.
for Giri-Grossman-Soffer-Zupan (GGSZ) method.
 and the relative
and the relative  conserving phase
conserving phase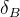 between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the
between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the  decay under investigation.
decay under investigation. The Gronau-London-Wyler (GLW) method (M. Gronau D. Wyler Phys.Lett. B265 (1991) 172; M. Gronau, D. London, Phys.Lett. B253 (1991) 483) is based on the reconstruction of the  decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay to
decay to  -even or
-even or  -odd eigenstates. The
-odd eigenstates. The  modes normally used are:
modes normally used are: 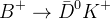 , with
, with  is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 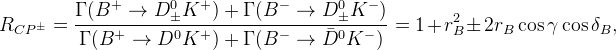
 This set can provide an information on
This set can provide an information on  ,
,  , and
, and  with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases.
with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases.
 decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay to
decay to  -even or
-even or  -odd eigenstates. The
-odd eigenstates. The  modes normally used are:
modes normally used are:  :
:  ,
,  ;
;  :
:  ,
,  ,
, 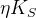 ,
, 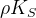 , and
, and 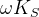 .
.
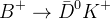 , with
, with  is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 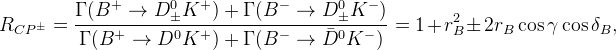
 This set can provide an information on
This set can provide an information on  ,
, 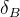 , and
, and  with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases.
with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases. In the ADS method, D. Atwood, I. Dunietz and A. Soni, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3257 (1997),  is measured from the study of
is measured from the study of  decays, where
decays, where  mesons decay into non
mesons decay into non  eigenstate final states. The suppression of
eigenstate final states. The suppression of  transition with respect to the
transition with respect to the 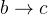 one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the
one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the  meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored
meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored 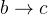
 decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed
decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed  decay, or through a suppressed
decay, or through a suppressed 
 decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored
decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored  decay. Neglecting
decay. Neglecting  -mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the
-mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the  measurement, the measured ratios
measurement, the measured ratios 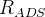 and
and 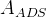 are related to the
are related to the  and
and  mesons' decay parameters through the following relations:
mesons' decay parameters through the following relations: ![R_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos\gamma\cos\delta),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_6f88dbde825ec879a69f94b702543683.png)
![A_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})-\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\sin\gamma\sin\delta)/R_{\rm ADS},](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_9c76bf82e9d7630117d2ae806cedd7c4.png) with:
with: 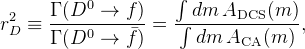
 In case of the
In case of the  analysis with
analysis with  we use the following ratios:
we use the following ratios: ![R^{\pm}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos(\gamma\pm\delta)),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41afc139cc9ed5b97c8bcc7e836d6ea5.png) The used observables are connected to the "classical"
The used observables are connected to the "classical"  and
and 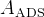 set by simple relations:
set by simple relations: 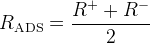 and
and  . The values of
. The values of 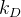 and
and  are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio
are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio  has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG.
has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG.
 is measured from the study of
is measured from the study of  decays, where
decays, where  mesons decay into non
mesons decay into non  eigenstate final states. The suppression of
eigenstate final states. The suppression of  transition with respect to the
transition with respect to the  one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the
one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the  meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored
meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored 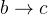
 decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed
decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed  decay, or through a suppressed
decay, or through a suppressed 
 decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored
decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored  decay. Neglecting
decay. Neglecting  -mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the
-mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the  measurement, the measured ratios
measurement, the measured ratios 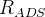 and
and 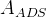 are related to the
are related to the  and
and  mesons' decay parameters through the following relations:
mesons' decay parameters through the following relations: ![R_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos\gamma\cos\delta),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_6f88dbde825ec879a69f94b702543683.png)
![A_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})-\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\sin\gamma\sin\delta)/R_{\rm ADS},](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_9c76bf82e9d7630117d2ae806cedd7c4.png) with:
with: 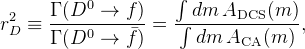
 In case of the
In case of the 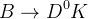 analysis with
analysis with  we use the following ratios:
we use the following ratios: ![R^{\pm}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos(\gamma\pm\delta)),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41afc139cc9ed5b97c8bcc7e836d6ea5.png) The used observables are connected to the "classical"
The used observables are connected to the "classical"  and
and 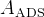 set by simple relations:
set by simple relations: 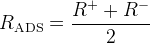 and
and  . The values of
. The values of 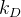 and
and  are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio
are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio  has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG.
has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG. The Giri Grossman Soffer Zupan (GGSZ), also called Dalitz method (A. Giri, Y. Grossman, A. Soffer and J. Zupan, Phys. Rev. D 68, 054018 (2003)) is based on the reconstruction of the  decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay
decay 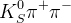 ; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 
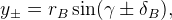
 decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay
decay 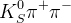 ; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 
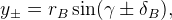
The angle  of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing
of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing  and
and  mediated transitions in
mediated transitions in  decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams:
decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams: 
 decay:
decay:  and the relative
and the relative  conserving phase
conserving phase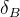 between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the
between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the  decay under investigation.
decay under investigation.
 of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing
of the CKM triangle can be measured comparing  and
and  mediated transitions in
mediated transitions in  decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams:
decays. The decays proceed through the following diagrams: 
 decay:
decay: - a singly Cabibbo-suppressed CP eigenstate, like
 for Gronau-London-Wyler (GLW) method;
for Gronau-London-Wyler (GLW) method; - a doubly Cabibbo-suppressed flavor eigenstate, like
 for Atwood-Dunietz-Soni (ADS) method;
for Atwood-Dunietz-Soni (ADS) method; - a Cabibbo-allowed self-conjugate 3-body state, like
 for Giri-Grossman-Soffer-Zupan (GGSZ) method.
for Giri-Grossman-Soffer-Zupan (GGSZ) method.
 and the relative
and the relative  conserving phase
conserving phase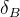 between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the
between the two amplitudes. These parameters depend on the  decay under investigation.
decay under investigation. The Gronau-London-Wyler (GLW) method (M. Gronau D. Wyler Phys.Lett. B265 (1991) 172; M. Gronau, D. London, Phys.Lett. B253 (1991) 483) is based on the reconstruction of the  decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay to
decay to  -even or
-even or  -odd eigenstates. The
-odd eigenstates. The  modes normally used are:
modes normally used are: 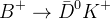 , with
, with  is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 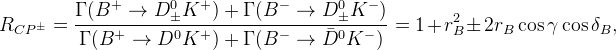
 This set can provide an information on
This set can provide an information on  ,
, 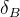 , and
, and  with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases.
with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases.
 decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay to
decay to  -even or
-even or  -odd eigenstates. The
-odd eigenstates. The  modes normally used are:
modes normally used are:  :
:  ,
,  ;
;  :
: 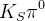 ,
,  ,
, 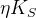 ,
, 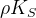 , and
, and 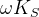 .
.
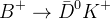 , with
, with  is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
is also reconstructed. The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 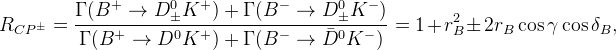
 This set can provide an information on
This set can provide an information on  ,
, 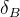 , and
, and  with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases.
with an 8-fold ambiguity for the phases. In the ADS method, D. Atwood, I. Dunietz and A. Soni, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3257 (1997),  is measured from the study of
is measured from the study of  decays, where
decays, where  mesons decay into non
mesons decay into non  eigenstate final states. The suppression of
eigenstate final states. The suppression of  transition with respect to the
transition with respect to the 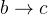 one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the
one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the  meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored
meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored 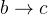
 decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed
decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed  decay, or through a suppressed
decay, or through a suppressed 
 decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored
decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored  decay. Neglecting
decay. Neglecting  -mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the
-mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the  measurement, the measured ratios
measurement, the measured ratios 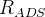 and
and 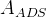 are related to the
are related to the  and
and  mesons' decay parameters through the following relations:
mesons' decay parameters through the following relations: ![R_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos\gamma\cos\delta),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_6f88dbde825ec879a69f94b702543683.png)
![A_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})-\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\sin\gamma\sin\delta)/R_{\rm ADS},](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_9c76bf82e9d7630117d2ae806cedd7c4.png) with:
with: 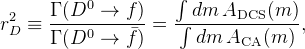
 In case of the
In case of the 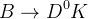 analysis with
analysis with  we use the following ratios:
we use the following ratios: ![R^{\pm}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos(\gamma\pm\delta)),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41afc139cc9ed5b97c8bcc7e836d6ea5.png) The used observables are connected to the "classical"
The used observables are connected to the "classical"  and
and 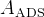 set by simple relations:
set by simple relations: 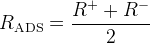 and
and  . The values of
. The values of 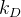 and
and  are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio
are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio  has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG.
has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG.
 is measured from the study of
is measured from the study of  decays, where
decays, where  mesons decay into non
mesons decay into non  eigenstate final states. The suppression of
eigenstate final states. The suppression of  transition with respect to the
transition with respect to the 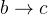 one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the
one is partly overcome by the study of decays of the  meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored
meson in final states which can proceed in two ways: either through a favored 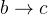
 decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed
decay followed by a doubly-Cabibbo-suppressed  decay, or through a suppressed
decay, or through a suppressed 
 decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored
decay followed by a Cabibbo-favored  decay. Neglecting
decay. Neglecting  -mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the
-mixing effects, which in the SM give very small corrections to \g\ and do not affect the  measurement, the measured ratios
measurement, the measured ratios 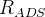 and
and 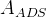 are related to the
are related to the  and
and  mesons' decay parameters through the following relations:
mesons' decay parameters through the following relations: ![R_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos\gamma\cos\delta),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_6f88dbde825ec879a69f94b702543683.png)
![A_{\rm ADS}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{+}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})-\Gamma(B^{-}\rightarrow [f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}{\Gamma(B^{+}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{+})+\Gamma(B^{-}\to[\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{-})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\sin\gamma\sin\delta)/R_{\rm ADS},](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_9c76bf82e9d7630117d2ae806cedd7c4.png) with:
with: 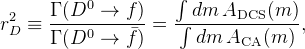
 In case of the
In case of the 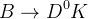 analysis with
analysis with  we use the following ratios:
we use the following ratios: ![R^{\pm}=\frac{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\rightarrow [\bar f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}{\Gamma(B^{\pm}\to[f]_{D^{0}} K^{\pm})}=(r_{B}^2+r_{D}^2+2 r_{B} r_{D} k_{D}k_{B}\cos(\gamma\pm\delta)),](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_41afc139cc9ed5b97c8bcc7e836d6ea5.png) The used observables are connected to the "classical"
The used observables are connected to the "classical"  and
and 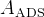 set by simple relations:
set by simple relations: 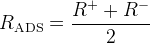 and
and  . The values of
. The values of 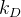 and
and  are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio
are taken from our study of charm mixing or the CLEO-c collaboration results. The ratio  has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG.
has been measured in different experiments and we take the average value from PDG. The Giri Grossman Soffer Zupan (GGSZ), also called Dalitz method (A. Giri, Y. Grossman, A. Soffer and J. Zupan, Phys. Rev. D 68, 054018 (2003)) is based on the reconstruction of the  decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay
decay 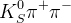 ; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 
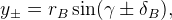
 decay to
decay to  , where
, where  and
and  decay
decay 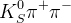 ; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way:
; The four observables for this method are formed in the following way: 
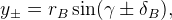
View topic | View difference side by side | History: r22 < r21 < r20 < r19 | More topic actions
Powered by
 Ideas, requests, problems regarding this web site? Send feedback
Ideas, requests, problems regarding this web site? Send feedback
 Ideas, requests, problems regarding this web site? Send feedback
Ideas, requests, problems regarding this web site? Send feedback

![\,\gamma [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_346b4369d40fd8964bda0f769a5b4bbe.png)

![\,\delta_{B}(DK) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_de1251af0a072fb83f6dd951669769db.png)



![\,\delta_{B}(DK^{*}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_5164e268a514bb26250f2bad6b8038e2.png)



![\,\delta_{B}(D^{*}K) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_59f1351d3c4dd771bf1d0e886a13457a.png)




![\,\delta_{B0}(DK^{0}) [^{\circ}]](/foswiki/pub/UTfit/GammaFromTrees/_MathModePlugin_5e88e4e05fc48c6d86a012b46b14cf1b.png)